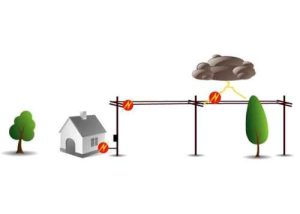
Indirect lightning strike
Indirect lightning strikes are the result of a direct lightning strike whose flow has not been controlled. Any lightning current whose path is not properly controlled is called indirect lightning
In a typical thundercloud, the upper part, made of ice crystals, is generally positively charged, while the lower part, made of water droplets, is negatively charged. By influence, the lower part of the cloud leads to the development of charges of opposite signs (therefore positive on the part of the ground which is nearby).
Electrical exchanges occur within this cloud, but also between different clouds of the same type. This results in lightning. However, the cumulonimbus cloud also behaves like a giant flat cloud-to-ground capacitor.

Indirect lightning strikes are the result of a direct lightning strike whose flow has not been controlled. Any lightning current whose path is not properly controlled is called indirect lightning

Known since time immemorial, lightning presents numerous dangers to property and living beings. A direct lightning strike is the encounter between a descending leader and an ascending leader originating from a natural trigger.
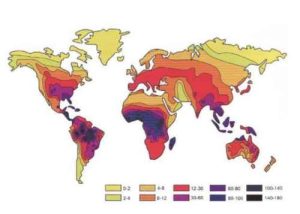
Up to 100 lightning strikes occur every second on the Earth's surface. The study of this phenomenon highlights three main categories of risks stemming from

Formation of a storm cloud: The presence of unstable, humid, and warm air masses leads to the formation of storm clouds: cumulonimbus clouds. This type of cloud