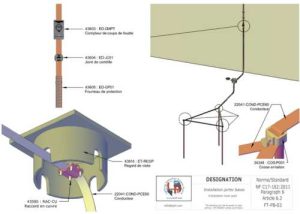
The grounding system for a lightning rod plays a crucial role in the overall lightning protection system. Here are its main functions:
Dissipation of Lightning Energy:
The grounding system allows the electrical energy of lightning to be safely dissipated into the ground. When a lightning rod detects a lightning strike, it directs this massive energy to the earth through a system of conductors. The grounding system is the final element that receives this energy and distributes it into the ground.
Damage Prevention:
By directing lightning energy away from structures, grounding helps prevent physical damage to buildings, such as fires or structural damage. It also protects internal electrical and electronic systems from lightning-induced power surges.
Personal Safety:
Grounding is essential for the safety of a building's occupants. By ensuring efficient dissipation of lightning energy, it minimizes the risk of electric shock or other lightning-related hazards for people inside the building.
Compliance with Standards:
Lightning protection standards, such as NF C 17-102 in France or IEC 62305 internationally, stipulate specific requirements for grounding systems. Compliance with these standards ensures that lightning protection systems meet safety standards.
Electromagnetic Interference Reduction:
A good ground connection helps reduce electromagnetic interference that can be generated by lightning discharge, thus protecting sensitive equipment.
Electrical System Stability:
Grounding contributes to the overall stability of a structure's electrical system by providing a return path to the ground for electrical currents.
For these reasons, an effective and well-designed grounding system is an essential component of any lightning protection system, ensuring the safety and protection of structures, equipment and people against the destructive effects of lightning.